The Role of Plyometrics in Speed Training

Plyometrics play a crucial role in speed training by enhancing explosive power and acceleration. These exercises engage fast-twitch muscle fibers, which directly contribute to improved sprinting efficiency and coordination. By utilizing the stretch-shortening cycle, plyometrics promote neuromuscular adaptations, increasing your ability to absorb and reapply force. Integrating various plyometric exercises into your regimen can yield significant performance gains. There’s much more to discover about how plyometrics can transform your speed training regimen.
Understanding Plyometrics: What Are They?
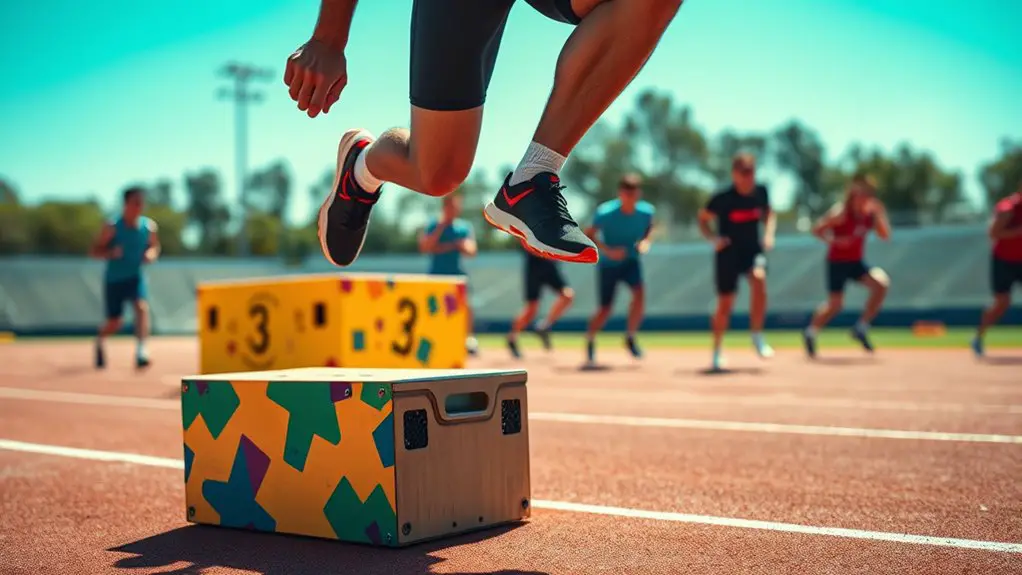
Plyometrics, often referred to as jump training, are exercises that leverage the stretch-shortening cycle of muscle contractions to enhance power and speed. This training method has roots in the 1960s and gained popularity through various athletic disciplines, reflecting a rich plyometric history. The concept originated in Eastern Europe, where coaches recognized the benefits of explosive movements for improving athletic performance.
You can implement numerous training variations within plyometrics, including depth jumps, box jumps, and bounding exercises, each targeting specific muscle groups and movement patterns. These variations can be tailored to your athletic needs, allowing for a progressive overload approach that maximizes power output. Furthermore, understanding the mechanics of these exercises is vital; the rapid stretch of a muscle prior to contraction considerably contributes to increased force production. By integrating plyometric training into your regimen, you can enhance your speed and agility, leading to improved performance in your chosen sport.
The Science Behind Plyometric Training
While many athletes may view plyometric training as simply a series of explosive jumps, the underlying science reveals a complex interplay of biomechanics and neuromuscular adaptations. When you perform these high-intensity movements, your muscles undergo rapid stretching followed by immediate shortening, a phenomenon known as the stretch-shortening cycle. This cycle enhances your muscle’s ability to generate explosive strength, vital for sprinting and jumping.
Research indicates that plyometric training greatly improves the rate of force development, enabling faster acceleration and improved overall speed. The neuromuscular adaptations from this training include increased motor unit recruitment and enhanced intermuscular coordination, allowing your body to produce more powerful muscle contractions. Additionally, plyometrics promotes elastic energy storage in your muscles and tendons, further contributing to explosive performance. Understanding these scientific principles can help you leverage plyometric training effectively to maximize your speed potential.
Key Benefits of Plyometrics for Speed Development

The benefits of incorporating plyometric training into your speed development regimen are numerous and well-supported by research. Plyometrics enhance your explosive strength, which translates to improved acceleration and top-end speed. Studies have shown that these high-intensity, high-velocity movements activate fast-twitch muscle fibers, important for speed enhancement.
Additionally, plyometric benefits extend to neuromuscular efficiency; by training your body to utilize elastic energy during rapid movements, you enhance overall coordination and reaction times. This can lead to better performance not just in sprinting but in various sports requiring quick bursts of speed.
Furthermore, plyometric training increases your body’s ability to absorb and reapply force, which is fundamental for maximizing sprinting efficiency. Regularly integrating plyometrics into your workouts can lead to significant improvements in your sprinting capabilities and overall athletic performance, making it a essential component in any speed training program.
Essential Plyometric Exercises for Athletes
Incorporating a variety of essential plyometric exercises into your training routine can greatly enhance athletic performance. These exercises focus on explosive movements, which are vital for improving speed and agility. Here are three key types of exercises to include:
- Bounding Drills: These enhance stride length and frequency, promoting better running mechanics.
- Jump Variations: Incorporating box jumps or depth jumps can develop power and explosiveness, translating to faster sprinting.
- Single-leg Hops: These improve balance and strength, important for maintaining speed during dynamic movements.
Research shows that plyometrics activate fast-twitch muscle fibers, leading to improved force production and athletic output. By regularly integrating these exercises, you’ll build the necessary strength and explosiveness to excel in sports, ultimately translating to enhanced speed on the field or court. Prioritize technique and progression to maximize benefits and reduce injury risk.
How to Integrate Plyometrics Into Your Training Regimen

Integrating plyometrics into your training regimen requires a strategic approach to maximize performance benefits while minimizing injury risk. Begin by selecting appropriate plyometric variations, such as box jumps, depth jumps, and bounding, that align with your athletic goals.
To optimize training frequency, aim for 1-3 sessions per week, allowing adequate recovery between sessions. Here’s a sample integration plan:
| Day | Activity Type | Plyometric Variation |
|---|---|---|
| Monday | Strength Training | Box Jumps |
| Wednesday | Speed Work | Depth Jumps |
| Friday | Agility Drills | Bounding |
Incorporating this structured approach fosters improved explosive strength and speed while reducing the likelihood of overtraining. Remember to monitor your body’s response and adjust training volume accordingly to maintain performance and health.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Plyometric Training
When engaging in plyometric training, improper form execution can greatly hinder your progress and increase injury risk. Additionally, insufficient recovery time between sessions not only compromises performance but also affects long-term adaptation. It’s essential to recognize these common mistakes to optimize your training outcomes and enhance speed effectively.
Improper Form Execution
Although plyometric training can greatly enhance speed and power, improper form execution often leads to suboptimal results and increased injury risk. To maximize the benefits of plyometrics, it’s essential to focus on proper technique. Common mistakes include:
- Improper landing: Landing with stiff legs or an incorrect foot position can lead to joint strain and a loss of power.
- Inadequate knee alignment: Allowing the knees to collapse inward during jumps can increase the risk of knee injuries.
- Insufficient depth in jumps: Failing to properly utilize the stretch-shortening cycle limits the effectiveness of the exercise.
Insufficient Recovery Time
Insufficient recovery time is a critical oversight in plyometric training that can undermine performance and increase injury risk. When you engage in high-intensity exercises, your muscles require adequate recovery to repair and adapt. Failing to implement effective recovery strategies—such as proper rest intervals, active recovery sessions, and nutrition—can lead to fatigue, reduced explosiveness, and compromised form. This not only hampers your training balance but also elevates the likelihood of overuse injuries. Research indicates that a minimum of 48 hours between intense plyometric sessions is essential for ideal recovery. By prioritizing recovery, you guarantee your body can perform at its best, maximizing the benefits of plyometrics in speed training while minimizing injury risks.
Measuring Progress: Evaluating the Impact of Plyometrics

To effectively gauge the impact of plyometric training on speed development, you’ll want to utilize a combination of quantitative assessments and performance metrics. These tools will serve as vital progress indicators, allowing you to evaluate your improvements over time. Consider implementing the following evaluation metrics:
Utilize quantitative assessments and performance metrics to track your plyometric training progress effectively.
- Vertical Jump Height: Measure changes in your vertical leap to assess explosive strength.
- Sprint Times: Track your 20m or 40m dash times to determine speed enhancements.
- Reactive Strength Index (RSI): Analyze your ability to shift from eccentric to concentric movements efficiently.
Success Stories: Athletes Who Transformed Their Speed With Plyometrics
You might be surprised to learn how elite sprinters have harnessed plyometrics to achieve remarkable speed improvements. Case studies show significant gains in sprint times and explosive power, underscoring the effectiveness of these training methods. Additionally, athletes in team sports have reported enhanced agility and acceleration, showcasing the versatility of plyometrics in various athletic contexts.
Elite Sprinters’ Transformations
While many athletes rely on traditional training methods to enhance their speed, elite sprinters are increasingly turning to plyometrics to achieve remarkable transformations. These athletes leverage plyometric training methods to improve their explosive power and sprinting efficiency, ultimately refining their elite sprinting techniques.
Consider the following successes:
- Improved acceleration: Athletes have reported faster starts and quicker shifts during races.
- Enhanced stride length: Plyometrics help in increasing stride frequency, allowing sprinters to cover more ground efficiently.
- Injury resilience: Strengthening muscles and tendons through plyometrics reduces injury risk, enabling consistent training.
These transformations illustrate how incorporating plyometrics can lead to significant advancements in speed, making it an essential component of any elite sprinter’s training regimen.
Team Sports Success Stories
Plyometrics have proven beneficial not only for elite sprinters but also for athletes in team sports looking to enhance their speed. Numerous case studies highlight how incorporating plyometric training dramatically improves acceleration and overall agility, essential for effective game strategies. For instance, a soccer team integrated plyometrics into their regimen, leading to a 15% increase in sprint times, which strengthened their offensive capabilities and improved team dynamics. Similarly, basketball players who focused on explosive movements saw enhanced vertical leaps and quicker shifts during games. These changes not only elevated individual performance but also contributed to cohesive gameplay, allowing teams to execute strategies more efficiently. Therefore, plyometrics serve as an important tool in optimizing speed and agility within various team sports contexts.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Plyometrics Be Harmful to Beginners?
Yes, plyometrics can be harmful to beginners if not approached carefully. It’s essential you prioritize injury prevention by focusing on proper form and technique. Without mastering the basics, the risk of strain or injury increases greatly. Start with low-impact exercises to build a foundation before advancing to more explosive movements. Gradually incorporating plyometrics into your routine can enhance performance while minimizing potential harm, provided you listen to your body and progress appropriately.
How Often Should Plyometric Workouts Be Performed?
You might think plyometric workouts are too intense for regular practice, but finding the right balance is key. Frequency guidelines suggest incorporating these workouts 1 to 3 times a week, depending on your fitness level. Each session should last about 20 to 30 minutes, allowing for adequate recovery. This approach helps maximize benefits while minimizing injury risk, ensuring you build explosive strength safely and effectively as part of your broader training regimen.
Are There Age Restrictions for Plyometric Training?
When considering age restrictions for plyometric training, it’s essential to assess youth athletes’ development. Generally, younger athletes should wait until they’ve established a solid foundation in strength and coordination before engaging in high-impact plyometrics. Age considerations often suggest starting around ages 12 to 14, depending on physical maturity. However, individual assessment is key, as each athlete’s readiness can vary greatly, influencing their safety and effectiveness in plyometric exercises.
Can Plyometrics Improve Endurance as Well as Speed?
Imagine your body as a finely tuned engine, capable of both speed and endurance. Plyometrics can indeed enhance your endurance benefits, especially when incorporating various plyometric variations like depth jumps or box jumps. These exercises not only improve muscle power but also increase your aerobic capacity by engaging fast-twitch fibers and promoting better oxygen utilization. This dual focus helps you sustain performance over longer durations, making plyometrics a valuable tool for overall athletic enhancement.
What Equipment Is Needed for Plyometric Exercises?
For effective plyometric exercises, you’ll need specific plyometric equipment like a sturdy box for box jumps, resistance bands for added resistance, and a jump rope for agility. Safety precautions are essential; guarantee your equipment is stable and appropriate for your fitness level. Additionally, wearing supportive footwear can help prevent injuries. Incorporating these elements can enhance your plyometric training while minimizing risk, allowing you to focus on improving your performance safely.





